The potential of Layer 2: Savings on Ethereum Fees and Reduced Energy Consumption and Transaction Time

Due to the exponential growth of use cases using the Ethereum Mainnet, and the increasing popularity of projects (i.e., CryptoKitties, and other NFTs and the DeFi boom), the actions towards the scalability of the network have been gaining momentum.
The urgency for the scalability relies not only on the increasing gas (transaction) fees but also on the capability of the network to compete with current systems while allowing the new generation of finance and digital assets to operate at its best. Currently, Ethereum has a throughput of 15 transactions per second (TPS) when payment providers such as Visa can make almost 6,000 TPS (Statista, 2022).
To address these issues, Ethereum proposed Ethereum 2.0, a network development that changes the consensus protocol from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake and adds sharding, which greatly increases the speed and throughput by 133x-266x TPS.
The evolution of the Ethereum blockchain is planned and being executed in stages, due to the complexity of the changes. However, in the meantime, the size of the ecosystems and communities building several business cases using this blockchain has not stopped growing.
Hence, trying to solve the current issues of slow transactions and high fees, many decentralized applications started implementing layer 2 solutions using horizontal scaling to solve the same problem.
Today there are several solutions to choose from to scale the usability of Ethereum through a layer 2, that are built on top of the execution chain of Ethereum. Additionally, for most of these solutions, the future merger will allow the continuity of the execution, since they are built on top of Ethereum. And what is more interesting, at the end, Eth2 and Layer 2 complemented each other working alongside to solve scalability issues.
Layer 2 increases, even more, the scalability of Ethereum (Ethereum, 2020; Finematics, 2021) making it possible to achieve hundreds of thousands and even a million transactions per second surpassing payment providers like Visa, Union Pay, MasterCard, and others without compromising security or decentralization. It makes Ethereum blockchain great for future applications. For businesses using the ethereum blockchain, it means a robust underlying system that allows faster and cheaper transactions.
This article explains what a layer 2 solution is, why it is important and provides an explanation of the main differences among scaling solutions, their advantages, and disadvantages.
What is layer 2?
According to Ethereum (2021), layer 2 constitutes all solutions designed to scale decentralized applications (dapps) by handling transactions off the Ethereum Mainnet (layer 1) while benefiting from Ethereum mainnet security model. As previously discussed, these solutions aim to address the transaction speed, network congestion, and increasing gas fee that is currently polluting layer 1.
“Is a way to scale blockchains increasing the throughput and transactions per second. There are two ways to scale it, scaling the base itself or scaling the network by offloading the work to another layer, layer 2.”- Ethereum, 2021.
Why is it important?
A layer 2 is important because it provides additional scalability to Ethereum passing from 15 transactions per second (TPS) to 2,000-4,000 TPS depending on the layer 2 solution maintaining the properties of the Ethereum blockchain in terms of security and decentralization. It is worth mentioning Ethereum is already working on a scaling solution that involves the change from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake and the use of sharding which in combination with a layer 2 solution might increase throughput to almost a million transactions per second (Finematics, 2020).
Layer 2 solutions
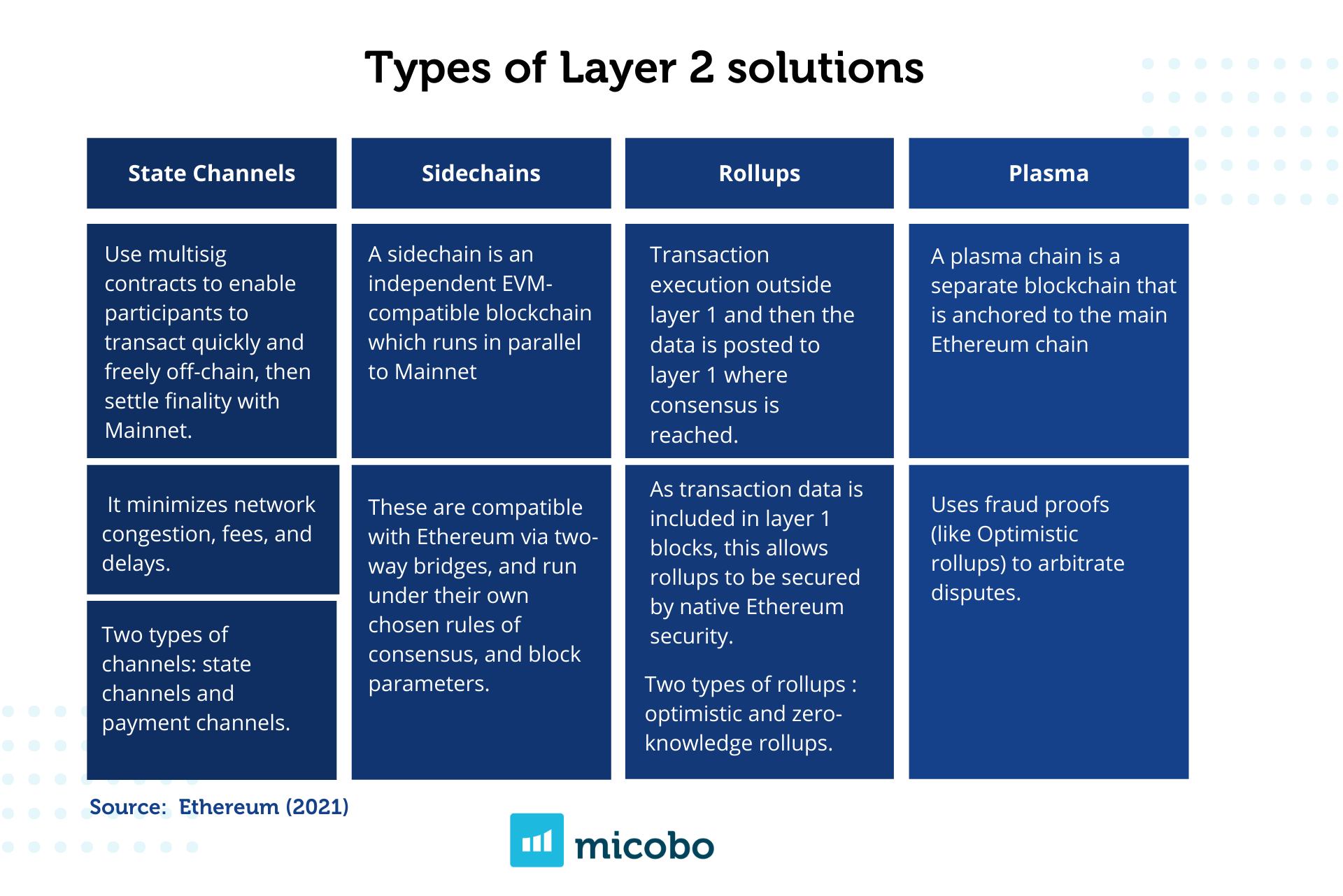
There are different types of layer 2 solutions. Channels, Sidechains, Rollups and Plasma, being rollups one of the most popular solutions due to their compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) making it easier for developers to migrate decentralized applications to layer 2, reducing fees for users, allowing open participation and fast transaction throughput (TPS).
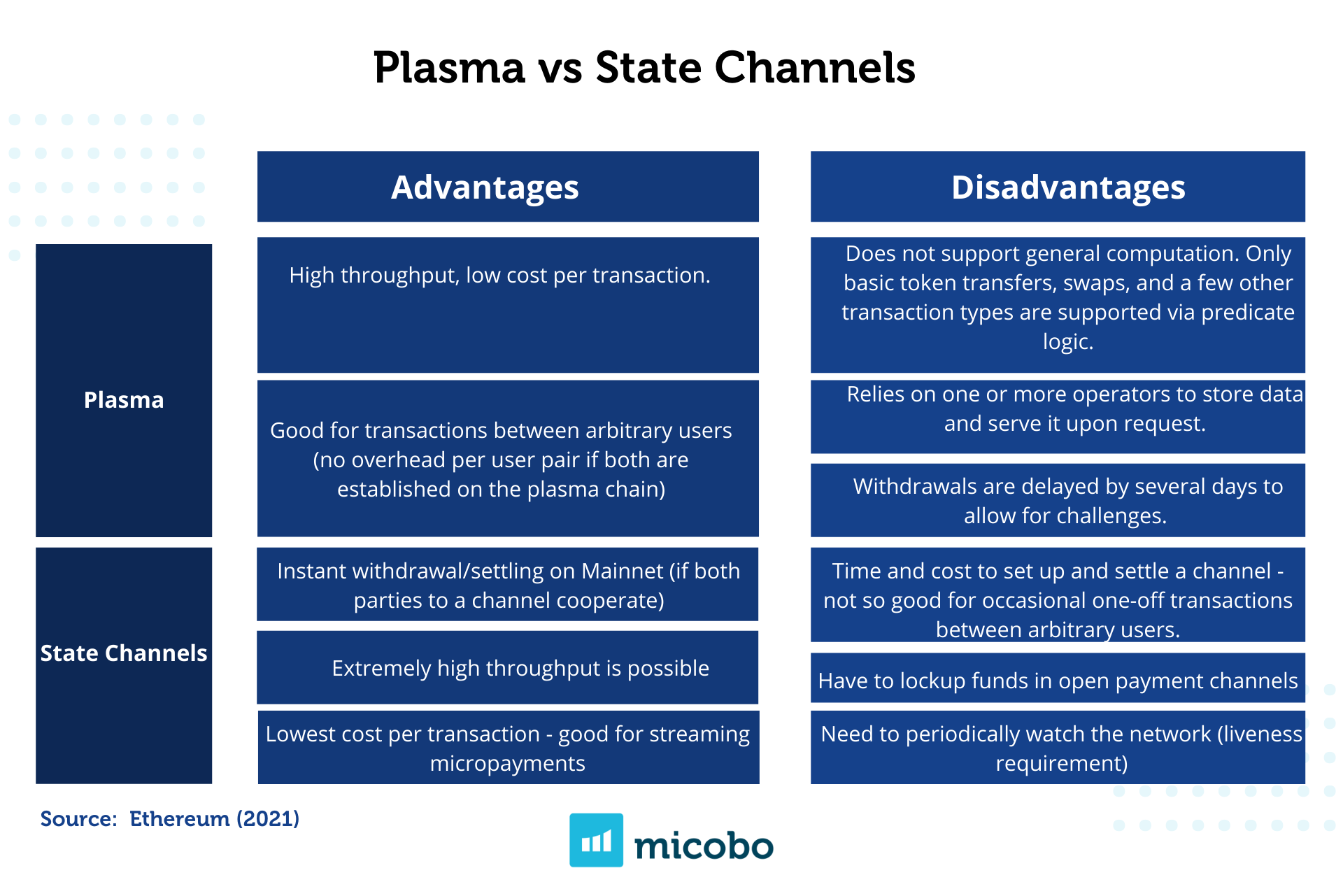
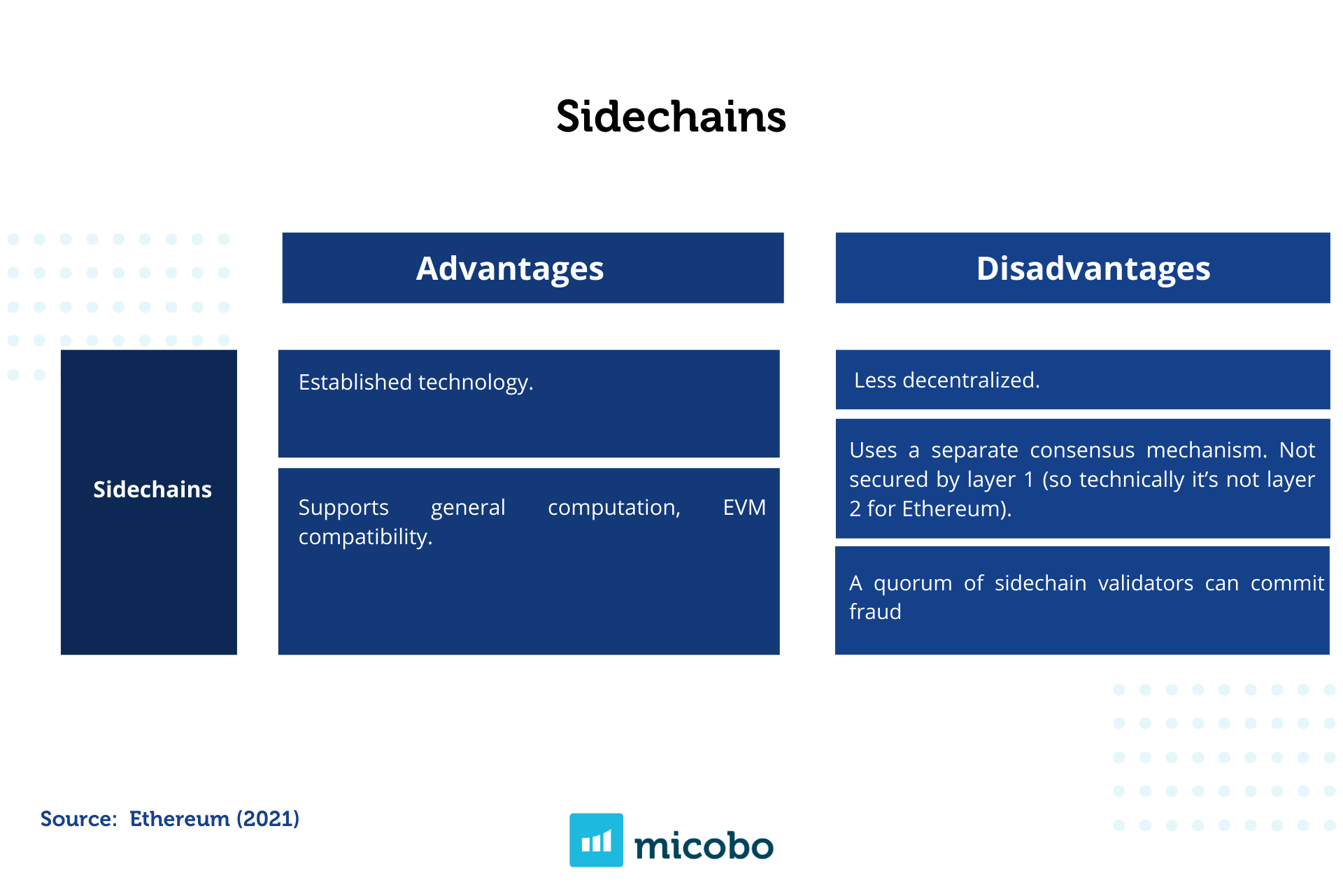
Channels are fully secured by Ethereum, however, it works well only for a specific set of applications as payments. Sidechains, on the other hand, are EVM compatible and can scale general purpose applications, but they are less secure than another layer 2 solutions because they do not rely on the security of Ethereum, and instead, they have their own consensus protocol (Finematics, 2020). Plasma chains provide high throughput at a low cost per transaction, nevertheless, it does not support general computation, and only basic token transfers, swaps and a few other transaction types are supported via predicate logic.
Rollups are a general-purpose scaling solution that relies on Ethereum security with the advantage of deploying all of the existing smart contracts without sacrificing security and with little or no changes. A rollup is a scaling solution that executes transactions outside of Ethereum but post transaction data on Ethereum. It basically can execute transactions in the rollup, takes the data, compresses it, and rolls it up to the Ethereum mainchain in a single batch, meaning it moves computation off-chain allowing more transactions to be processed (See Figure 1). In addition, “each rollup deploys a set of smart contracts on Ethereum that are responsible for processing deposits and withdrawals and verifying proofs”- Finematics, 2020.
Figure 1. Rollup scaling solution process. Source: Finematics (2021)
The discussion defining the best scaling solution is mixed (Ethereum, 2020). It depends on the needs of every application, on the purpose (payments, exchanges, universal, NFTs, Treasury), on the resources (usually zk-rollups need more computational capacity for their validity proofs), on the risks.
What is certain in the Ethereum community is that zero-knowledge rollups are increasing in popularity due to new developments in progress improving the compatibility to EVM (which is one of the main issues given the complexity of the technology ). Vitalik Buterin, and many other developers see zk-rollups as a long-term scaling solution (Ethereum, 2020).
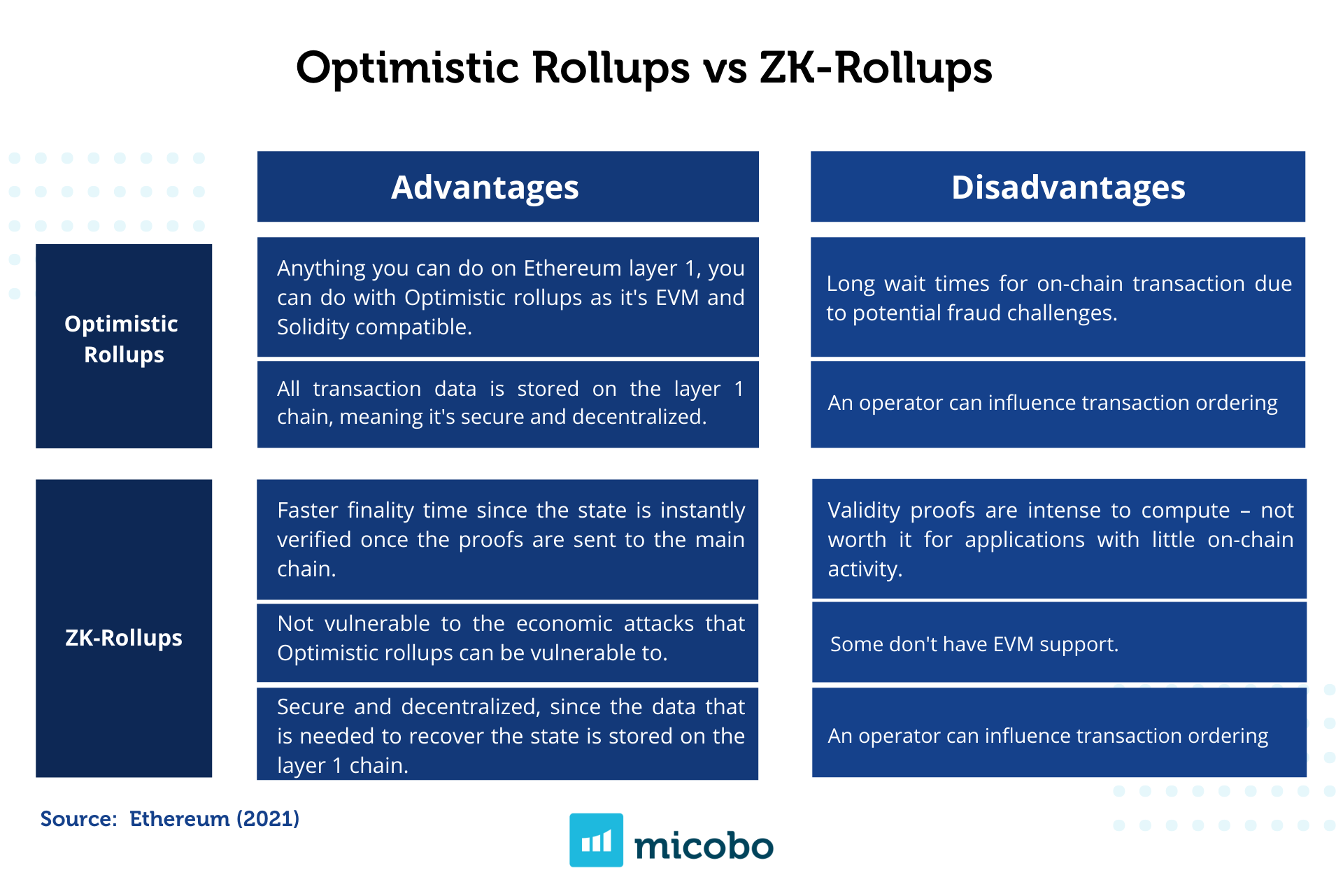
In retrospect, Layer 2 is an excellent solution to provide additional scalability to Ethereum and applications need to take into account the advantages and disadvantages of every scaling solution. With this article, one could think that ZK-Rollups are the best scaling solution. Nevertheless, if the purpose of an application is payments and the application is for basic tokens, one could use Plasma. The selection of the scaling solution is directly related to the needs of the decentralized application and it is up to companies to decide what is best for their business and customer experience.
To see an analysis of the differences between Optimist Roll-Ups and Zero-Knowledge Rollups and the most popular providers, wait for our next article.
About micobo
micobo GmbH is a leading European software company for Security Token Offerings and Blockchain Software Development (DLT). It provides fully compliant software solutions for Security Token Offerings and advises on structuring DLT- and Blockchain-based Securities. micobo empowers financial institutions with state-of-the-art technology focusing on providing a better customer experience and achieving measurable results.
Bibliography
- Ethereum. Layer 2 Rollups. 2021. Retrieved from https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/scaling/layer-2-rollups/. Last Accessed 12.01.2022.
- Ethereum. Plasma chains. 2021a. Retrieved from https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/scaling/plasma/. Last Accessed 12.01.2022.
- Ethereum. Plasma chains. 2022. Retrieved from https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/scaling/sidechains/. Last Accessed 12.01.2022.
- Ethereum. State Channels. 2022a. Retrieved from https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/scaling/state-channels/. Last Accessed 12.01.2022.
- Ethereum. A rollup-centric ethereum roadmap. 2020. Retrieved from https://ethereum-magicians.org/t/a-rollup-centric-ethereum-roadmap/4698. Last Accessed 12.01.2022.
- Finematics. Ethereum Layer 2 Scaling Explained. 2020. Retrieved from https://finematics.com/ethereum-layer-2-scaling-explained/. Last Accessed 12.01.2022.
- Gluchowski, Alex. Evaluating Ethereum L2 Scaling Solutions: A Comparison Framework. 2021. Retrieved from https://blog.matter-labs.io/evaluating-ethereum-l2-scaling-solutions-a-comparison-framework-b6b2f410f955. Last Accessed 17.01.2022.
- L2Beat. Finances and Risks. 2022. Retrieved from https://l2beat.com/. Last Accessed 12.01.2022.
- Statista. Visa, MasterCard, UnionPay transaction volume worldwide 2014-2020. 2022. Retrieved from https://www.statista.com/statistics/261327/number-of-per-card-credit-card-transactions-worldwide-by-brand-as-of-2011/. Last Accessed 12.01.2022.
